Saturday, August 11, 2007
Bye bye and Thanks
First, I would like to thank Drs. Wang and Frayer for instituting such a program – I absolutely loved my experience this summer. There was so much I learned about medicine, surgery, health care, how engineers fit into health care, human dynamics, myself, etc., etc… not to mention, being able to enjoy New York City in the summertime. If you haven’t noticed…this summer was priceless for me and I am very grateful to have had this opportunity. I also would like to thank Dr. Grant for being my mentor. Although, I enjoyed surgery in general, I found a special enjoyment out of plastic surgery and I think that can be attributed to having a great mentor and plastics squad.
I hope everyone else had as great of a time as I did this summer and best of luck to all of the future participants in the program. Get involved and enjoy the experience, you will probably never do anything like it again. That’s it all...for now...
Tuesday, August 7, 2007
Final Week of Summer Immersion...Tear
Anyway, as I showed in my presentation my research project basically consisted of a literature review and case study analysis to form the foundation for a prospective investigation of Dr. Grant’s. He wants to assess the effect short pulsed electromagnetic fields have on post-op breast augmentation patients. I won’t go into everything that I presented on; however, some of the more interesting findings were as follows. First, was a meta-analysis of over 30 years and 50 clinical trials on both bone and soft tissue revealing that ALL studies were methodologically flawed…awesome. I’m glad published research is so well reviewed…and carried out for that matter. Some of the flaws were huge, too – like no control groups or errors in the protocols. Honestly, I thought that was outrageous. Nonetheless, these were studies from years ago, and a lot of the newer studies are much better designed. Several of the better, more recent articles showed that in vitro and in vivo PEMF stimulated the synthesis and upregulation of various growth factors, such as, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and transforming growth factor (TGF). These growth factors then act to induce cellular proliferation, angiogenesis, stimulation of an immune response, deposition of ECM and wound contraction. In other words, they aid in wound healing and in turn should also help reduce pain in human subjects by speeding up the healing process. The chart below illustrates an increase in tensile strength of rat wounds treated with PEMF for 21 days post-op as compared to the negative controls. Signal I, II, III, and IV are simply varying doses of PEMF; whereas the "Sham" is the negative control.
A company called Ivivi Technologies in
The electric field induces a magnetic field and the device is laid on the wounded area, applying the desired PEMF therapy directly onto the patient’s wounds. It’s a non-invasive therapy that allegedly reduces pain and speeds along the healing process, allowing for an earlier discharge, and thus, cutting costs, too…that is if it actually works. A cool idea. But, it just looks so bogus to me. Anyway, the company has just released news that they have an IRB-approved, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial on 30 ischemic cardiomyopathy patients (decreased blood flow to the heart) who are not candidates for surgical procedures. If it works in these cases, that would be absolutely great…it could reduce the number of many invasive, difficult cardiac surgeries. Personally, I think the biggest obstacle with this technology will be convincing the general population that a stupid wire with a flashy LED on it will actually save you…
Sunday, August 5, 2007
Some thoughts about surgical staplers
Surgical staplers and clip appliers are complex mechanical medical devices that have been on the market for years and are mature in their technology. These devices are used in gastrointestinal, gynecologic, thoracic, and many other surgeries to remove part of an organ, to cut through organs and tissues and to create connections between structures. The benefit of using these devices allows for more complex procedures and shorter surgical procedure time.
However, Each year over the past 5 years there have been 8,000 to 9,000 adverse event reports related to surgical staplers. The most common problems with the device are: staples don't form, staplers misfire or don't fire. The most common problem with the patient is anastomosis failure. This is also where my research project originally arise from. Solving the anastomosis problem is meaningful.
In the OR, I also saw electronic surgical staplers. Compared to mechanical stapler, it provides improvements such as, removes force from the anastomotic site; digitally senses tissue compression levels; digitally selects staple heights; prompts surgeon via LCD and voice message.
By talking to the doctors and the engineers from the vendors, I feel that the research in a medical device company is somewhat different from research in the school. In the school, the research is more focused on the basic science, but in a company, it must be application oriented. For example, the physical principles inside a stapler have been well established since Newton and Maxwell. However, such a device is still innovative because it facilitates doctor’s procedures, and it fundamentally changed suturing process. The research is a designing process. Instead of incorporating a lot of high technologies, a device that best meets the doctor’s need might be more useful.
Friday, August 3, 2007
Neurological Surgery
Neurological Surgery
I also have been working on my clinical research project evaluating effectiveness of two different treatments for aneurysms, and have obtained some interesting results. I will be presenting my research project in the seminar meeting in
Overall, I gained a lot from this experience, especially in terms of realizing that there are many areas that still need technological improvements. I would like to thank my clinician mentor, Dr. Riina, and also Dr. Gobin and Dr. Chapple.
Thursday, August 2, 2007
Vascular Wrap-up
Week 7
The Last Post
Last time I left a taunting message about my research—now it’s time for some results! It turned out that the average age of the last menses was 48 and that surgery would occur within 20-29 years after this age with 99% statistical confidence. This identified the patient population with ages 68-77. The HRT data revealed that there was no significant difference between patients on HRT vs. not for primary patency while patients with osteoporosis were worse-off than those without osteoporosis. This is interesting data that may suggest that patients with osteoporosis who undergo vascular procedures should have more frequent patency check-ups.
This is the last post for me! One thing that I pulled away from this experience is that I do not want to be a doctor, at least not a surgeon! They have an intense lifestyle to say the least, and they basically live at the hospital. Otherwise I had a chance to see some great technology and procedures that I wouldn’t be exposed to anywhere else, and living on the Upper East Side rent-free was unbeatable. Thanks to Dr. Vouyouka, and thanks for reading!
Surgery and Adios
The summer immersion program is almost over now, and I think that I did gain a better understanding of clinical practice. I am fairly sure this experience will spill over into my current collaborations, and will benefit me. It also gave me a better understanding of the need to be assertive. The programs structure does need refinement, however, but it is not a loss, especially if one tries to gain specific insight on one’s own. It would have been nice if the exact clinical experiences we were expected to have (and it did feel as if there explicit expectations) would have been spelled out clearly before hand.
I’m looking forward to returning home to my wife and child tomorrow. Happy 1st birthday, Aiden!
Mitral Valve Replacement (MVR)
Finally, I convinced myself to watch at least one open heart surgery. I was surprised at how invasive the whole procedure was. The doctors’ basically sedated the patient, sliced his chest open, and then pulled his ribs apart using their bare hands or a crude mechanical device. It was almost like watching a scene out of a movie with hygienic zombies in scrubs trying to carefully eat the victim’s heart. Okay, maybe that’s an exaggeration. What followed was a bit more impressive. They bypassed the patient’s arteries, immobilized the heart using high concentration of potassium chloride, and then made an incision in the heart in order to replace the mitral valve. The following picture is borrowed from its.med.yale.edu. It depicts a mitral valve replacement.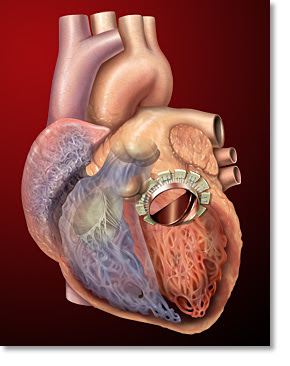 Apparently, this particular patient had mitral valve regurgitation. This was evident from his transesophogeal echocardiogram or the ultrasound measurements. One could see that the oxygenated blood that entered the left ventricle through the mitral valve periodically reentered the left atrium. In most cases, a patient’s valve is irreversibly compromised due to either ischemia, stenosis, or infection. These problems are usually onset due to coronary artery disease, age, or rheumatic fever, respectively. However, congenital defects are not rare.
Apparently, this particular patient had mitral valve regurgitation. This was evident from his transesophogeal echocardiogram or the ultrasound measurements. One could see that the oxygenated blood that entered the left ventricle through the mitral valve periodically reentered the left atrium. In most cases, a patient’s valve is irreversibly compromised due to either ischemia, stenosis, or infection. These problems are usually onset due to coronary artery disease, age, or rheumatic fever, respectively. However, congenital defects are not rare.
In the patient’s case, the problem was caused by ischemia through coronary artery disease. As a result, the doctor had decided to replace his valve with a bovine valve - the reasons for choosing a bovine valve or a mechanical valve were explained previously by Dickinson. It seemed as though the stitching of the valve required great dexterity. One of the more skilled residents tried to stitch the valve but it seemed as though he could not make the more difficult 10-12 o’clock stitches. As a result, the primary surgeon took over and showed him how it should be done.
One could definitely make it easier for these doctors by developing an innovative device for sewing. In fact, I don’t really know why a big hospital like NYP still uses open heart surgery for such cases. There are hospitals that are performing these types of procedures percutaneously using the da Vinci surgical system. I think that’s the way to go. If not, the least one should do is make something that replaces the “needle and string.”
My Last Week in Plastics
First the discussion was on different types of reductions, mainly different types of incisions and techniques used to reduce the breast size. Then there was a good discussion of how to decide what type of reduction the patient will receive. Specific cases are discussed and the idea of what is realistic and what is not was gone over. Many of the scars after the surgeries are quite noticeable. Images from : www.aboardcertifiedplasticsurgeonresource.com.

 Generally, an incision is made around the nipple and the nipple is then removed and a new nipple relocation is added to raise the nipple site to fit with the new smaller breast. Tissue is removed along with skin and then brought in downward to close over and shape the new breast. Scars will remain around the nipple, extended to the crease, and through the crease as seen in the pictures. Later that day, a patient came to office hours to be consulted for a breast reduction. Mistakes were also discussed where the reduction produced breasts that were very asymmetric and occasionally with nipples that were misplaced. Many of these complications arise because the doctor works with an assistant on one side or because of shifts from laying on teh operating bed to getting up. This really brought the talk together because I went from the academic discussion to the patient doctor interactions.
Generally, an incision is made around the nipple and the nipple is then removed and a new nipple relocation is added to raise the nipple site to fit with the new smaller breast. Tissue is removed along with skin and then brought in downward to close over and shape the new breast. Scars will remain around the nipple, extended to the crease, and through the crease as seen in the pictures. Later that day, a patient came to office hours to be consulted for a breast reduction. Mistakes were also discussed where the reduction produced breasts that were very asymmetric and occasionally with nipples that were misplaced. Many of these complications arise because the doctor works with an assistant on one side or because of shifts from laying on teh operating bed to getting up. This really brought the talk together because I went from the academic discussion to the patient doctor interactions. Additionally, I attended the M&M meeting Monday evening were complications for the past month in the plastics department were discussed. No patients died of complications, but additionally surgeries were required. In one case a tissue expander became infected after only a week and after taking intravenous antibiotics the patient opted to have the expander removed.
At office hours I was able to the progress of the patient I spoke about last entry and the V.A.C. has continued to help in wound closure progress. I also helped to remove sutures. The patient had a cut that ran down the side of the face and a second cut on the upper back. A running stitch was used to close the face face wound.
I also attended a butt flap surgery where a patient had gotten a bed ulcer after lying on their back for an extended amount of time. In order to close the wound the muscle above the wound was mobilized and swung down to close over the wound.
I have also spent time working on the Case Report that I am writing up. I have submitted a draft to the Chief Resident that I am working with to get feedback on format and wording.
Code Blue in the OR
During this week I was able to observe a few more surgeries and attend a few more rounds. I was luckily able to scrub into another tracheaesophageal fistula. The patient was two days old and had a type C fistula which consists of an upper esophagus ending in a blind pouch and a connection between trachea and fistula. Dr. Spigland was able to occlude the fistula and connect the esophagus back together.
However, during the esophageoesophagus connection the patient’s lung did not infant. The lung appear very deflated and small. A code blue was called and within 1-2 minutes a barrage of nurses, residents, and attendings came to help out. They ran into the room with concern expressions and eagerness to help out. The attendees quickly got the patient to start breathing again using manual ventilation. There was a pediatric cart in the room in case the use of a defiberator was needed. In actuality, most of the people who rushed in for the code blue just stood around watching while 1-2 attendees did all the work. But it’s a good sign when over a dozen people rush into the room minutes after a code was called.
I was able to make progress on my research and conclude some aspects of the project. I will continue to collaborate with Dr. Spigland on the research project dealing with esophageal atresia and hopefully write something up in the near future.
Wednesday, August 1, 2007
Calcium Score: Part 2
 Maybe it is better in a certain way that I will not be collecting scores using VCAR. According to my mentor, although the software is more advanced than Smart Score, it is just as tedious to use. If you recall, the Smart Score software forced one to highlight the calcium in transverse CTA slices. It, thereby, was able to deduce a calcium score based on just volume (volumetric score) or area and average Hounsfield value (agatson number) for the overall calcium in the arteries. VCAR calculates the score in a similar fashion, but it does not need the user to highlight the calcium. Instead, it is designed to automatically segment the calcium in the arteries. However, before the algorithm is capable of doing this, one must click along the centerline of an artery so that the algorithm can basically fit a curve to the selected points and subsequently subtract it from the image to straighten out the artery. Then it presents the artery of interest in a longitudinal format so that one is better able to view the calcium deposits (figure). I’m not certain why this step is necessary. Nevertheless, the software seems very user friendly so I think it would have been fun to work with.
Maybe it is better in a certain way that I will not be collecting scores using VCAR. According to my mentor, although the software is more advanced than Smart Score, it is just as tedious to use. If you recall, the Smart Score software forced one to highlight the calcium in transverse CTA slices. It, thereby, was able to deduce a calcium score based on just volume (volumetric score) or area and average Hounsfield value (agatson number) for the overall calcium in the arteries. VCAR calculates the score in a similar fashion, but it does not need the user to highlight the calcium. Instead, it is designed to automatically segment the calcium in the arteries. However, before the algorithm is capable of doing this, one must click along the centerline of an artery so that the algorithm can basically fit a curve to the selected points and subsequently subtract it from the image to straighten out the artery. Then it presents the artery of interest in a longitudinal format so that one is better able to view the calcium deposits (figure). I’m not certain why this step is necessary. Nevertheless, the software seems very user friendly so I think it would have been fun to work with.
Tuesday, July 31, 2007
Neurological Surgery
I was able to go to NICU (neonatal ICU) rounds this past week. Unlike neurological surgery rounds, which only last about 30 minutes, the NICU rounds lasted more than 2 hours. The two were quite different not only because of the age of patients, but also it seemed that in the NICU, rounds were focused on determining the day’s treatment for the patient as well as assessing each patient’s day to day progress, whereas in neurological surgery rounds were focused on just assessing progress. The cases in the NICU were striking in demonstrating the fragility of life, and how important treatment in the beginning of life is.
Neurological Surgery
One surgical procedure I observed this week which was particularly interesting was an endoscopic resection of a colloid cyst. First, some definitions are needed – a colloid cyst is a slow-growing non-malignant tumor that is usually located in the third ventricle of the brain. The cysts are composed of a cell layer on the outside of the cyst and a creamy-like colloid in the center. The colloid cyst can block drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and cause hydrocephalus.
MRI image of colloid cyst in the third ventricle. http://neurosurgery.ucla.edu
The treatment options for a colloid cyst include putting in a shunt to drain the CSF or surgery to remove the cyst. Surgery can either be done by a craniotomy or through the less invasive endoscopic technique that I observed. The endoscopic resection technique involves drilling a small centimeter diameter burr hole in the skull, then putting an endoscope with a camera through the hole (see picture). The cyst location is constantly irrigated from outside to maintain a clear view. Several small instruments are guided through the tubes in the endoscope to cut and burn the tissue. Then, several holes are made in the cyst cell wall. A suction catheter is used to suck away the colloid material from the cyst. A balloon catheter is inserted inside the cyst and inflated. The catheter is removed, taking cyst wall material with it. At the end of the procedure, the doctor then uses the bipolars to burn any remaining cyst which may not have been removed. I found the suction procedure quite interesting because sometimes, the doctor would start to suck non-colloidal material into the suction tube, and then would immediately stop the suction. It seems that it would be quite easy to make mistakes with this technique if the doctor is not well-trained, which is why this procedure is only performed at select hospitals.
Image of an endoscope passing through a burr hole in the skull. http://neurosurgery.ucla.edu
Colloid cyst viewed through an endoscope. http://neurosurgery.ucla.edu
The risks associated with ionizing radiation
According to the FDA, there are two categories of risk associated with ionizing radiation: 1)Overdiagnosis of benign incidents and unnecessary followup tests and 2) acute and chronic biological damages associated with radiation. The excitation and ionization of molecules and atoms in the body can produce free radicals, break chemical bonds, and cross-link macromolecules. That's why the effects of radiation exposure are not necessarily immediate. In general, radiation sensitivity of bodily tissues depend on two factors: 1) the rate of proliferation and 2) its degree of differentiation. Thus, tissues with a lot of blood supply (i.e. proliferative capability) are most radio-sensitive and tissues that are far advanced (i.e. nervous tissue) are the least sensitive. Unfortunately there has not been extensive studies to evaluate the relationship between radiation exposure and chronic biological effects such as cancer induction. Therefore, any data available in this regard is based on the conservative notion that any amount of ionizing radiation is harmful to the body. Keep in mind that all of the numbers in this post are national estimates.
Radiologists use different jargon to measure radiation. There is what is called absorbed dose, which is simply amount of energy deposited per unit mass of matter with units in Gray (Gy) or mGy. Then is equivalent dose which measures the "biological effects" of the absorbed dose to each tissue of the body. This parameter is a product of absorbed dose and a factor called "radiation weighing factor" which takes into account the radio-sensitivity of different tissues. The final and most important parameter is the effective dose which is the weighted average of absorbed doses to all bodily tissues. For CT, in order to calculate effective dose one has to integrate the dose profile along a line parallel to the axis of rotation of the gantry and devided by the nominal thickness of the slice. However, since this is a bit complicated, physicists introduced a new term called the CT dose index (CDTI) which is measured experimentally. A 100mm ionization chamber will be placed in the center of a head and body phantom and the absorbed dose in measured at the center and periphery. A specific ration of these two values are added up to give a two dimensional weighted average of CTDI. When this number is divided by pitch (ratio of the distance the patient has moved through the scanner per rotation, per slice thickness) then you will have a volumetric absorbed dose. Once you multiply this CTDI(vol) by the length of scan and the radiation weighing factor for the specific tissue you are scanning, you have the effective dose in units of seivert or mili-seivert (mSv).
Now some interesting numbers and statistics....
The effective dose of a regular chest x-ray is 0.02 mSv, or if you get a dental x-ray your bone marrow is exposed to 0.094 mSv. If you get a regular chest CT (high resolution) you are exposing yourself to 500x more radiation than a chest x-ray (10 mSv) while if you get a head CT you are exposing yourself to 100x more radiation than a chest x-ray.
We are all exposed to background radiation due to sources other than medical imaging modalities (shown bellow). The annual background radiation in the USA is around 3.0 mSv. So a regular chest CT is equivalent to 3.3 years worth of background radiation. This will increase your chances of getting cancer by 0.04% (with natural cancer risk being 20.6%).

National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements, Bethesda, MD
Monday, July 30, 2007
Cardioplegic Solutions

Cardioplegia in Latin cardio means heart and plegia means paralysis. Therefore, cardioplegic solution is a solution that paralyzes the heart. The solution is mixed with blood and infused into the coronary circulation to induce and maintain paralysis while the heart is being operated on. Perfusion of cardioplegic solution through heart stops the myocardium contraction/ relaxation, reducing its metabolic requirements. During this paralysis period, the heart is uniquely endowed with anaerobic pathways that it uses for energy production. To reduce the body's( heart and brain mainly) metabolic demands, the temp. is dropped from 37.5 to 22 degrees celsius and the heart is injected with the cardioplegic solutions every 40 mins for upto 120 mins. This temp. drop is known to reduce the rate of ischemia by 50%, which is a great thing! Plegisol Solution is a combination of calcium chloride dihydrate, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, potassium chloride, and sodium chloride...Once the mycardium has been sutured and the normal intracellular/extracellular re-established, and the heart starts beating again! Amazing stuff..
Next time you come across this phrase remember heart paralysis!
Dickson
6th Week in Plastics
 The depth of the wound has decreased dramatically to about .5" deep. It is interesting to me that with a simple V.A.C. dressing the body is able to close over such a large open wound by itself. This week I helped in changing the V.A.C. dressing. First, we remove the old dressing and Dr. Spector cuts out in dead tissue as this will not help in wound closure. After debriding the wound, we place gauze in the wound and soak with Dakin's Solution. This is a aseptic solution for cleaning wounds what is made of sodium hypochlorite and boric acid (4 %). We allow the patient to sit our the 'rinse cycle' for a few minutes while the wound is soaked in Dakin's. Then we remove the soaked gauze and dry off the wound. The standard oval shaped black sponge is then cut to fit the wound. Often the doctor will cut the sponge half thickness and then cut out the pattern of the wound. This helps to keep the healthy tissue surrounding the wound health and increase drainage from the wound while promoting the granulation of the wound bed. A picture (from www.kci.com) is shown that pictorially shows how the fluid in the wound bed is able to exit through the black sponge and the vacuum is able to help in wound closure. Now that the patient has seen the wound closure capabilities of the V.A.C. and the wound has greatly decreased in size, there are now other options for closure of the wound. Because the patient has also lost weight over this time period, it may be possible to simply elevate the tissue on either side and close the wound. By leaving the V.A.C. on for a few more weeks, this would certainly be possible. It would also be possible, to put a skin graft over the wound to close it. As of now, the patient has opted to keep the V.A.C. dressing on and continue to allow the wound to make progress this way.
The depth of the wound has decreased dramatically to about .5" deep. It is interesting to me that with a simple V.A.C. dressing the body is able to close over such a large open wound by itself. This week I helped in changing the V.A.C. dressing. First, we remove the old dressing and Dr. Spector cuts out in dead tissue as this will not help in wound closure. After debriding the wound, we place gauze in the wound and soak with Dakin's Solution. This is a aseptic solution for cleaning wounds what is made of sodium hypochlorite and boric acid (4 %). We allow the patient to sit our the 'rinse cycle' for a few minutes while the wound is soaked in Dakin's. Then we remove the soaked gauze and dry off the wound. The standard oval shaped black sponge is then cut to fit the wound. Often the doctor will cut the sponge half thickness and then cut out the pattern of the wound. This helps to keep the healthy tissue surrounding the wound health and increase drainage from the wound while promoting the granulation of the wound bed. A picture (from www.kci.com) is shown that pictorially shows how the fluid in the wound bed is able to exit through the black sponge and the vacuum is able to help in wound closure. Now that the patient has seen the wound closure capabilities of the V.A.C. and the wound has greatly decreased in size, there are now other options for closure of the wound. Because the patient has also lost weight over this time period, it may be possible to simply elevate the tissue on either side and close the wound. By leaving the V.A.C. on for a few more weeks, this would certainly be possible. It would also be possible, to put a skin graft over the wound to close it. As of now, the patient has opted to keep the V.A.C. dressing on and continue to allow the wound to make progress this way.Additionally, this week I was able to attend a unilateral mastectomy. The patient has breast cancer in her right breast and decided that removing the breast was the best option. Dr. Spector counseled her on the different reconstruction techniques that can be used and allowed her to decide what would be best for her. The two main options are to complete an reconstruction by removing a portion of her abdomen and forming a breast from that or by simply placing a tissue expander in after the breast is removed. An example of a tissue expander is shown in the image on the right.
 With the first option, the procedure is called a free flap where tissue is taken from one part of the body and used in another, but it is moved with its own blood supply and hooked into the blood supply around the new site. For the tissue expander, the expander is placed under the muscle and slowly expanded by adding saline ever few weeks until the desired size is reached. Once the size is correct, implants are placed. In either case, addition surgery is required to reconstruct the nipple. In the OR, first the breast team comes in and removes the cancerous breast. The day prior to the surgery, the patient is injected with a dye which then accumulates in the nodes, which can easily be seen during surgery. An incision is made around the areola and then the skin is elevated off of the underlying breast tissue. The nipple and breast tissue are then removed. The nodes are then removed and sent to pathology. Frozen sections are taken and the surgery team is informed whether the cancer is present in the nodes. The sentinel lymph node is specifically checked. This is an indication as to whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Once the breast team has finished, the plastics people come to the OR and begin the reconstruction. The tissue expander is placed under the muscle with a small amount of saline in it. For the next few months the patient will come in periodically to have more saline injected into the expander. The port on the expander is labeled with a magnet so that Dr. Spector can use a magnet externally to locate the port.
With the first option, the procedure is called a free flap where tissue is taken from one part of the body and used in another, but it is moved with its own blood supply and hooked into the blood supply around the new site. For the tissue expander, the expander is placed under the muscle and slowly expanded by adding saline ever few weeks until the desired size is reached. Once the size is correct, implants are placed. In either case, addition surgery is required to reconstruct the nipple. In the OR, first the breast team comes in and removes the cancerous breast. The day prior to the surgery, the patient is injected with a dye which then accumulates in the nodes, which can easily be seen during surgery. An incision is made around the areola and then the skin is elevated off of the underlying breast tissue. The nipple and breast tissue are then removed. The nodes are then removed and sent to pathology. Frozen sections are taken and the surgery team is informed whether the cancer is present in the nodes. The sentinel lymph node is specifically checked. This is an indication as to whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Once the breast team has finished, the plastics people come to the OR and begin the reconstruction. The tissue expander is placed under the muscle with a small amount of saline in it. For the next few months the patient will come in periodically to have more saline injected into the expander. The port on the expander is labeled with a magnet so that Dr. Spector can use a magnet externally to locate the port.
Laparoscopic Surgery -- Removing Sigmoid Colon
This week I have a chance to observe Dr. Milson performs a laparoscopic surgery. When I entered the operation room, the surgery is already started. Everyone was pretty relaxed. The patient was lying on the operating table “sounds asleep”, while Dr. Milson was cracking joke and directing the residents what to do. When I walked close to the operating table, I saw there were various long rod-shaped surgical tools sticking from the abdomen of the patient’s body. Three physicians were holding these various surgical tools and watching the screen in front of them. One thing stand out is that the patient’s abdomen is swell like a balloon. Later I found out that in this kind of laparoscopic surgery, the abdomen is usually inflated with CO2, so the physicians have more room to work with. When I looked up at the screen, u can see all the guts of the patient. Also u can see the ends of the long surgical tools. Several of them are small clamps that use to hold different tissues. One scissor shaped tool is use to cut the connective tissue away from the sigmoid colon. It not only function as a scissor, but has some kind of heating mechanism that will seal the wound from the cutting so not much blood came out. It was quite amazing to see that how three physicians can work cooperatively to remove all the connected tissues from the sigmoid colon. Since it is already hard to maneuver using these long tools, and two people have to hold the tissue in place, so the other physician and cut them away from the colon. After the sigmoid colon is completely remove from the rest of the connective tissue, the doctor took the whole thing out from one of the incision of the body, and cut away the disease part. Then he used a special stable gun to join back the colon and the rectum. Finally, one of the residents performed a leak test to assure the colons are joined completely.
The whole procedure took about an hour and half, which is longer compared to traditional open surgery. However, there are several advantages. First, since only several small incisions are made during surgery, the recovery time will be shorter. Furthermore, blood loss will be minimal. One thing is quite remarkable in this type of surgery is the design of these various surgical tools used in the surgery.
Electrophysiology Lab
This week I went to electrophysiology (EP) lab in cardiology. In this laboratory, I mainly observed two procedures: implantation of a artificial pacemaker and Electrophysiology study.
The artificial pacemaker is a programmable device that generates electrical impulse to the heart to regular heart beats. The electrical signal is delivered by electrodes contacting the heart muscles. Usually people need a pacemaker when their own natural pacemaker is not working properly. When I first entered the EP Lab, they made me wear this 60 pounds lead to prevent radiation from the x-ray. It is quite tiring even wearing it for an hour, I must say quite admired these doctors are able to wear them all day long and perform operations.
The procedure itself is actually quite simple. The physician made a small incision on the right side of the upper chest, and then he threaded two special wires (in which the proximal tip contains an electrode) into the body and place the electrode near the heart muscle. Then he asked the assistant to generate different electrode signals through the wires and watch the pattern on the ECG. Then he adjusted the placement of the wires and repeated the signal generation several time till he got the desired ECG signals he wanted. Finally, he obtained a pacemaker and connected the wires into it and put the small device near the incision area. Then he secured the device under the skin and sewed up the wound. After the implantation is done, the physician went to a computer and remotely programmed the device.
From talking with the physician, I found out that these peacemakers generally last 5 to 10 years depending on the condition of the patient. Some patients like the one he just operated on only require pacing at certain time, but some other patients require the artificial pacemaker to work all the time.
The second type of procedure is an electrophysiology (EP) study. Normally, electricity flows throughout the atria first and then pause for a moment before the electric signal is propagate to the ventricles through the atria-ventricular (AV) node. The electrical signal brings about heart muscle contraction. The orderly pattern guarantees that the heart pumps blood efficiently. Whenever something wrong along the electrical conduction system, it causes a heart rhythm disturbance (termed arrhythmia), which will leads to inefficient pumping of the blood out to the body. The reason for an EP study is to find out the cause of such arrhythmia. Usually during an EP study, wires are placed on the sinus node (natural pacemaker), one on the AV node and one on the bundle of His (which is the wire that sends signal from AV node to the rest of ventricles). They also place several wires on the ventricles and atriums depending on situation. Then they will generate electrical signal on different places, and observed the corresponding signal recorded elsewhere to try to figure out the cause of the arrhythmia.
Sunday, July 29, 2007
Vascular Research
Vascular Surgery
Week 6
Vascular Research Project
My research project looks at the outcomes of vascular procedures in women. My surgeon mentor and others think that there may be a relationship between the outcomes of vascular procedures and hormone replacement therapy (HRT), osteoporosis, and menopause. “Outcome” is defined as patency—that is whether or not a vessel is open at a follow-up visit after surgery. After writing a script that was approved by the surgeons in charge, I called a list of about 300 elderly female patients (average age = 76) to ask them about HRT, osteoporosis, and menopause. Awesome!
The Patients
Some women were surprisingly sharp and inquisitive and really opened up to me over the phone. The responses were understandably colorful—if the patient felt better they exalted their surgeon while some patients with poor outcomes told me they had found new surgeons and hospitals entirely. Often the same surgeon was regarded in both positive and negative ways. This is understandable considering the variable difficulty in treatment that occurs between patients and procedures.
One thing that surprised me was that patients were very willing to open up to me over the phone—I heard some fascinating life stories. Alternatively some patients would not talk to me at all—they didn’t trust that I was calling from New York Presbyterian Hospital and requested a written questionnaire while others could only speak in Spanish. Other difficulties like disconnected telephone numbers and no answers left the respondents to about 30%. From these patients I got some interesting data regarding patency, HRT, and osteoporosis—really interesting data…that I can’t show you here because it might get published! Stay Tuned!
Two anastomosis devices

The first question is how to remove the colon. The magic gadget is called GastroIntestinal Anastomosis (GIA) device, which has two functionalities. First, it’s a cutting device that cut a piece of colon into two, as Shown in Fig. 1. At the same time, in order to prevent bleeding, it sutures the two edges of the cut simultaneously, as in Fig. 2. Two stagger rows of staples will be fired when the surgeon push the middle hidden blade to cut the colon. In this way, the entire colon can be removed easily and safely.
 The second question is how to connect the remaining part to the anal control muscle. This is more complicated. The End-to-End Anastomosis device has a detachable anvil at the distal end. To operate, the surgeon needs to put the anvil inside the remaining intestine and the EEA through the anus. Since both the anvil and EEA device have pointed piercing structure, they can connect to each other. After they are connected, squeeze the trigger to make a circular cut and anastomosis at the same time. Therefore, the remaining intestine is safely connected to the control muscle. After pull the entire device out from the anus, this step is finished.
The second question is how to connect the remaining part to the anal control muscle. This is more complicated. The End-to-End Anastomosis device has a detachable anvil at the distal end. To operate, the surgeon needs to put the anvil inside the remaining intestine and the EEA through the anus. Since both the anvil and EEA device have pointed piercing structure, they can connect to each other. After they are connected, squeeze the trigger to make a circular cut and anastomosis at the same time. Therefore, the remaining intestine is safely connected to the control muscle. After pull the entire device out from the anus, this step is finished.
A variety this week...
Outside the lab, I was able to observe a mastectomy with my homegirl Emily and my main man, Campolongo. The patient has cancer in her right breast and they were going to remove the breast tissue. I was amazed at how much tissue they took out. The next steps were to place an "expander" below here pectoral muscle for her future implant in a later surgery. Then within a couple months, she would have to undergo another surgery to have her nipple reconstructed. I had no idea that the whole process would take 3 operations. Another interesting procedure we got to see was how they determine what lymphnodes were more likely for infiltration. Apparently lymphnodes are most likely place for cancer to spread to. Prior to the surgery, a blue dye and a radio isotope is injected into the patient. I believe that is specific to the lymphnodes to areas surrounding the breast tissue. The blue dye is used to help the clinician find them. The radio isotope is used to determine how "hot" they are. From what I got, the hotter they are implies that they are more vascularized and more prone for cancer infiltration. However, the reading has no indication on whether the cancer has metastasized or not.
Next week I plan on joining Dr. Frayer and my main man Campolongo to observe little babies. Giddy up! Till then, I say "Good day!"
Friday, July 27, 2007
Rounds in Different ICUs, and the Horrible Monster that Haunts My Dreams
I am trying to write a Matlab program that can generate a two-dimensional airway model of the lungs, turn it into a mesh, and then export it in a form that is readable by Fluent. Right now, the hard part is trying to make it readable. Trying to reverse engineering the Fluent .msh file format is proving to be the bane of my existence. Instead of showing results, I chose to show the error message that I keep getting and a picture of a monster. If the error message had a representative monster, this is what it would look like.

Thursday, July 26, 2007
Ladies and Gentlemen, the results are in...
Unfortunately, I am unable to post the graphs from the preliminary data analysis, but it appears that the automatic segmentation algorithm lies somewhere between the phase contrast analysis and the manual segmentation. The manual segmentation tends to overestimate when compared to the other techniques, while the PC flow analysis tends to underestimate. Furthermore, the relation between all three is relatively linear, as indicated by a high correlation (0.95 or greater between any two of the three techniques) and a high level of confidence in the zero intercept inear regression.
And perhaps of the greatest importance, the technique demonstrates a "high degree of accuracy," as indicated by Dr. Weinsaft, when used to evaluate the cadiac metrics of subjects with Left Ventricle Disfunction (those who eject only a small portion of their blood in each cardiac cycle, on the order of 25% when compared to normal function of 50 or greater.) This has traditionally been one of the most time consuming
scenarios for a clinician to evaluate, so the time saving benefits from this automatic segmentation stand to be quite considerable.
Admittedly, the data set is still somewhat small (just 20 fully completed cases with an eventual target of 50 to 100). But the trends are already beginning to show. The next step, other than validation with more data sets, is to reconsider the design of the algorithm. As I mentioned before, which technique is more accurate? Phase contrast analysis or manual segmentation? Further, should the algorithm even emulate these techniques or should the design process be independent of other techniques? Perhaps a "true" measure should be experimentally derived using experimentation somehow?
The logistical hurdles of obtaining the truth are considerable. But for now, we are fairly convinced that the automatic segmenter operates consistly between the phase contrast measure and the magnitude measure, both of which are valid and widely used techniques in the clinical world.
Open Cholecystectomy





Gallbladder

So it turns out that a gallbladder can be removed and one can lead completely normal life without one, but under diets with less fat. This is because the primary function of a gallbladder is to store bile( for fat emulsification ) secreted in the liver. Having an inflamed gallbladder adds risks to liver inflammation and inflammation to other adjacent organs such as the pancreas.
Dickson
Catheter's in X-ray
As I mentioned previously, a lot of time is spent by radiologists doing intensive care unit imaging to make sure that every tube, line, and catheter is where it is supposed be. This is because if they aren't, complications and even death can occur. For example, its very important that feeding tubes end up in the stomach and not down one of the bronchi before you try to feed someone. But these reads are very time consuming, both in per scan rate and number of scans to read. So my research is focused on developing a method of computer aided detection of the tips, so that we at the very least can reduce the workload of the radiologists, which would further result in an increase in efficiency and throughput.
The first thing we looked at was that catheters were synthetic objects. They are basically tube with the ends cut off (kind of like a straw). This means that
1) The profile is consistent along its length
2) The profile of the object can known a priori
3) Intensity variations can be explained by
But we needed to verify the assumption so we took sample profiles along the length and got the graph below.

The profiles had roughly the same added attenuation at each point, the baseline is what mainly changed. So we are good to go on that front.
Taking into account the synthetic nature of the catheters, we developed a way to generate profiles automatically. These profiles are then matched from points outside the body to the tip, until no more evidence is found. We used normalized cross-correlation because it allowed for matching to occur regardless of intensity variations. Doing this progressive matching gave us results like the image below.

Not bad for proof of concept, right?
Luckily, I got to see many of the steps in how the images I am working with were acquired. This is actually quite helpful in knowing all the potential problems that the algorithm might need to deal with. I also spent time gathering data so that I have a larger set to work with. We are also planning on generating synthetic dataset next week to try out other methods of more direct detection.
CFD in Coronay Arteries: Part 1
Part 1: Segmentation
Thus far, I've only been able to complete part 1 (figure). Basically, I have created an interface that allows one to load CTA data, preprocess the data through numerous filters, and finally, segment the arteries of interest using a region growing algorithm and/or simple thresholding. The software is far from perfect since it performs the segmenation in 2D. That is, it segments the arteries slice by slice, causing the whole process of segmentation to be slightly tedious. Nevertheless, one can use it to reconstruct arteries of interest.
 Part 2: Tessellation
Part 2: Tessellation
Pending... I'm trying to tessellate the segmented volume with rectangles. The following depicts the grid for a straight pipe. Although it seems simple, it is really not for odd geometries.  Part 3: Computational Fluid Dynamics
Part 3: Computational Fluid Dynamics
If I get lazy, which I probably will, I plan to use a CFD software package like FLUENT. This sophisticated software package will allow me to simulate blood flow in reconstructed arteries of interest. The following is a simulation by some company (I can't find there link so if anyone knows where this is from, post it in the comments).
 Part 4: Validation and Index Development
Part 4: Validation and Index Development
I will validate the simulation by comparing theoretical fractional flow reserve values to practical ones (fraction of pressure about a lesion). And if the simulation proves to be incorrect, I will change the parameters of the mesh; otherwise, I will work on an index that decodes vulnerability.
J-Pouch
The operation was done laparoscopicly. The first part was as usual. Small holes were drilled on the abdominal wall and a 7cm incision was also made below the belly button. Large intestine and rectum were removed and taken out from the incision. However, the control muscle was kept, and this is the key point of the surgery.

After the removal of colon and rectum, the ileum was folded to form a reservoir. Later on, the bottom of the reservoir was connected to the control muscle. Sometimes, the second step requires two separate operations. After the reservoir is made, a temporary exit on abdomen is made so that the newly created reservoir isn’t in use immediately and may heal. 2 or 3 months after the first surgery, another operation closes the exit on abdomen.
The benefit of making a J-pouch is significant. The reservoir may store the waste until the need to have a bowel movement. The patient may have a pretty good control as normal people. It doesn’t need an external bag to store. Overall, the quality of life is enhanced.
Advanced Breast Reconstruction
The DIEP flap procedure essentially combines two procedures in one. The tissue harvested to reconstruct the breast comes from the patient’s belly fat. So the patient basically gets an abdominoplasty (tummy tuck) at the same time. No muscle is taken with this flap, just fat. The novelty of this procedure is that the blood vessels perforating through the rectus muscle (the deep inferior epigastric vessels) are clipped and subsequently microsurgically anastomosed to the internal mammary vessels to feed the transplanted tissue in a quasi-Frankenstein kind of way.
Figure 1. The deep inferior epigastric perforator vessels.
Figure 2. The internal mammary vessels.
It was really amazing to watch the microsurgery. Blood vessels were sutured together with these tiny needles and very thin thread…I couldn’t even see where the needle was…just an occasional flare of light as the shiny metal reflected the light from the microscope. The surgeons performing this operation were very skilled; it was amazing to watch them work.
So the end result looked something like this. Pretty cool.
Figure 3. Final result showing the anastomosis of the DIEP and internal mammary blood vessels.
Wednesday, July 25, 2007
Brain Lab
Week 5
Neuro Detour cont’d

The surgeon uses the fMRI interfacial data to ensure the tumor is removed completely. The above image shows some of the brain anatomy highlighted. This is a fantastic technology, and I think it’s important to point out that innovation can stem from existing technology that is applied in a novel way.
Hernia repair
My doctor performs surgeries twice a week. By far the most common surgery she performs are hernia repairs. There are at least 1-2 cases per day, so I have seen over a dozen different hernia repairs.
A hernia occurs when the contents of a body cavity bulges out into another area of the body. Sometimes they contain portions of intestines or body fat that are naturally lined to inside the cavity. Hernias are usually harmless, but they can potentially be dangerous if they cut off the blood supply.
There are many types hernias and can occur in different stages of your life. Some form during birth, others during fetal development, existing openings in the abdominal cavity or weakening in the lining, and conditions that cause added pressure on cavities. Some of these conditions are obesity, heavy lifting, coughing, fluid in the cavity, straining during bowel movements, and chronic lung disease.
The signs of a hernia can range from a painless lump or a painful, tender protrusion in the abdomen. The doctor can examine the area of pain by adding pressure to that area. From this the doctor will be able to determine if you do have a hernia.
If the hernia can cause the blood supply to be reduced, the hernia may need to be operated on. If the hernia is irreducible, emergency surgery may be needed. But if the attempt to reduce the hernia succeeds, surgery can be scheduled later.
In a hernia repair surgery, the surgeon makes a cut over the area of the hernia. The bulging tissue or organ is placed back inside the muscle wall, the muscle tissue is repaired, and the skin is closed. In many inguinal hernia repairs, a small piece of plastic mesh is used to repair the defect in the muscle tissue.
Laparoscopic Myotomy
Laparoscopy describes a group of operations performed with the aid of a camera placed in the abdomen. The laparoscope was first combined with a video camera in the 1980s, an accomplishment that helped free up the surgeons' hands, so they could better work with their instruments. The laparoscope also allows doctors to perform minor surgeries with just a small cut in the abdomen. This technique is known as laparoscopic-assisted surgery.
Laparoscopic myotomy refers to a laparoscopic-assisted surgical procedure in which a muscle is cut. The case that I observed in the OR involved the cutting of the muscle from the esophagus to the stomach (a disorder called esophageal achalasia). Achalasia is a disorder of the esophagus. The esophagus is less able to move food toward the stomach, and the muscle from the esophagus to the stomach does not relax as much as it needs to during swallowing. This relaxation is needed to allow food to enter the stomach.

Diagnosis
Barium Swallow - Patients are asked to swallow a liquid which will be visible on an X-ray. A series of X-rays are then taken. Achalasia patients will often demonstrate abnormal valve relaxation and an absence of normal contractions.
Esophageal Manometry - Pressure recordings are assessed in this exam through a small catheter placed into the esophagus. Characteristic findings in patients with achalasia include an elevated lower valve pressure and failure of the valve to relax with swallowing.
Endoscopy - This is a procedure in which a small, flexible telescope is passed through the mouth into the esophagus. The lining of the esophagus can then be examined and biopsied.
Treatment
Medical therapy for achalasia with drugs that relieve the spasm of the sphincter (the muscle between esophagus and stomach) has largely been unsuccessful and associated with numerous side effects. The classical method for treatment remains endoscopic balloon dilatation and surgery. While dilatation can achieve a good result in up to 60% of patients, the results are frequently not durable. Also, dilatation carries the risk of esophageal perforation which would require emergency surgery.
Historically, definitive surgical treatment for patients with achalasia included a formal rib spreading incision to perform an esophageal myotomy or splitting of the abnormally thickened esophageal muscle at the lower sphincter. Recent improvements in laparoscopy have allowed for significant advances in the treatment of achalasia. NYP is currently performing a laparoscopic myotomy for most of the achalasia patients. This approach requires small abdominal incisions for the placement of a camera and telescopic instruments. The abnormally thickened muscle surrounding the esophagus is incised to allow for improved swallowing. After completion of this myotomy a loose stomach wrap is created around the esophagus to minimize reflux.
Length of stay has been reduced to two days with minimal post-operative discomfort. Also, patients are tolerating regular food at the time of discharge.











